Circular Economy Introduction
What is The Circular Economy?
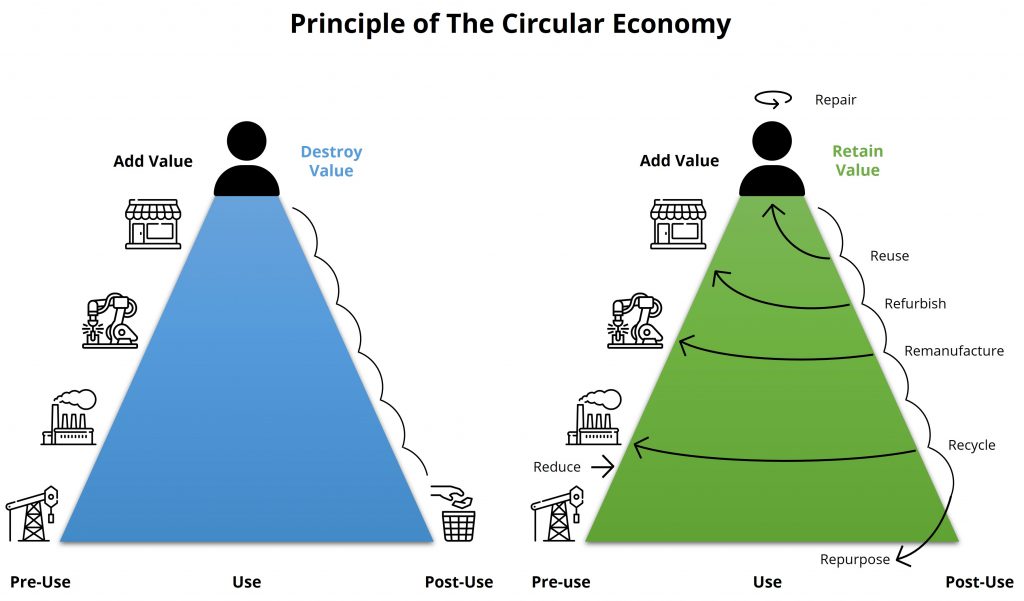
The Circular Economy (CE) is an innovative approach to production and consumption that aims to minimize waste, extend the lifecycle of materials, and promote sustainable resource use. Unlike the traditional linear model of “take, make, dispose,” CE focuses on designing products for longevity, reusing materials, and regenerating natural systems. By implementing circular strategies—reduce, reuse, repair, repurpose, recycle, refurbish, remanufacture—businesses and communities can reduce environmental impact, drive economic efficiency, and foster long-term sustainability. This transition is essential for tackling global challenges like resource scarcity, climate change, and waste management while creating new opportunities for innovation and value creation.
Following our Learning Path!
In our first section, you can learn about the principles and concepts of the Circular Economy and win the bronze badge upon completion.
In our second section, you will gain in-depth knowledge about the DECIDE toolbox and it’s potential. Preparing you perfectly for developing and validating Circular Economy Business Models. This will reward you with a silver badge.
This last section will guide you through a training case – putting your previously akquired knowledge to a test and help you get some hands-on experience in using all the tools within the Toolbox. This will, of course, leave you with the DECIDE gold expert status!





